Introduction
A bright, white smile is often associated with health, youthfulness, and attractiveness. However, over time, various factors can cause teeth to become discolored or stained, leading many individuals to seek teeth whitening treatments to restore the brightness of their smiles. Teeth whitening is a popular cosmetic dental procedure that effectively lightens the color of the teeth, resulting in a more radiant and confident smile. In this blog, we will explore the science behind teeth whitening, understand how it works, and delve into why it’s an effective method for achieving a whiter smile.
Understanding Tooth Discoloration
Before delving into the science of teeth whitening, it’s essential to understand the factors that contribute to tooth discoloration. Teeth can become stained or discolored due to a combination of extrinsic and intrinsic factors:
a. Extrinsic Factors:
External factors such as consuming dark-colored foods and beverages (e.g., coffee, tea, red wine), smoking, and poor oral hygiene can lead to surface stains on the enamel.
b. Intrinsic Factors:
Intrinsic discoloration occurs within the tooth structure and can be caused by factors such as aging, certain medications, dental trauma, and excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development.
The Science of Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening treatments work by employing various chemical agents to break down and remove stains from the tooth surface and, in some cases, from within the tooth structure. Two primary methods of teeth whitening are widely used: in-office professional teeth whitening and at-home teeth whitening kits.
a. In-Office Professional Teeth Whitening:
In-office professional teeth whitening is performed by dental professionals and involves the application of a higher concentration of bleaching agents compared to at-home kits. The most commonly used bleaching agent is hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which breaks down into hydrogen peroxide when applied to the teeth.
The process typically involves the following steps:
Dental examination:
The dentist evaluates the patient’s oral health to ensure they are suitable candidates for teeth whitening.
Gum protection:
The dentist applies a protective gel or barrier to the gums to shield them from the bleaching agent.
Bleaching gel application:
The bleaching gel, containing hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, is applied to the teeth.
Activation:
Some in-office treatments use special lights or lasers to activate the bleaching agent, accelerating the whitening process.
Reapplication (if necessary):
Depending on the degree of discoloration, the bleaching gel may be reapplied one or more times during the session.
Rinse and reveal:
After the desired level of whiteness is achieved, the gel is rinsed off, and the results are revealed.
b. At-Home Teeth Whitening Kits:
At-home teeth whitening kits are typically provided by dental professionals and contain lower concentrations of bleaching agents. The kits often include custom-fitted trays or strips that the patient applies at home.
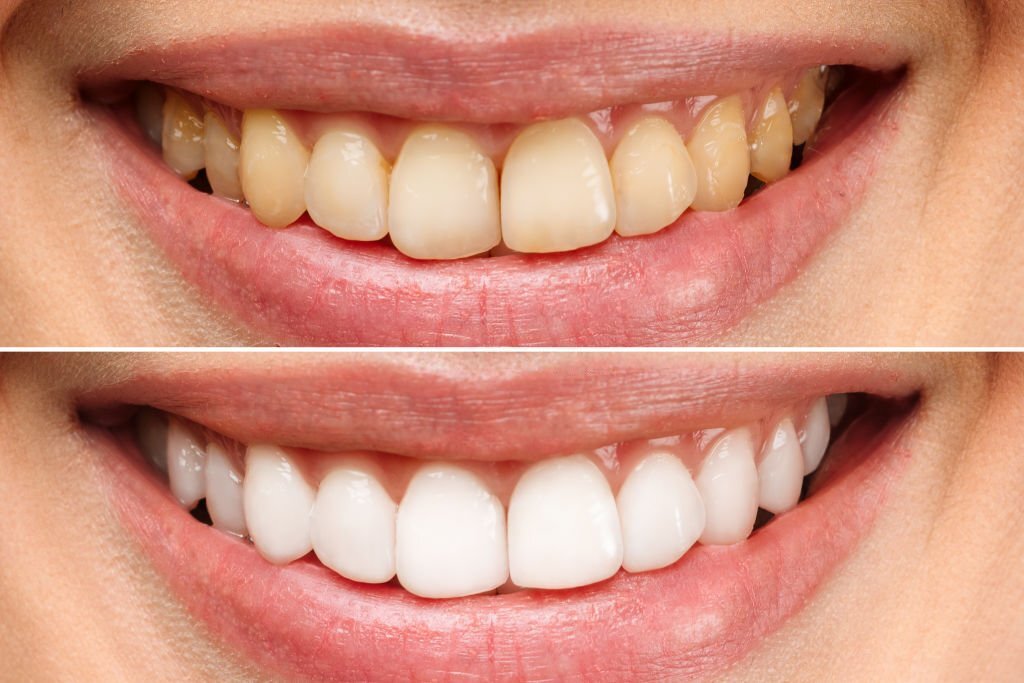
The process for at-home teeth whitening typically involves:
Dental examination:
The dentist evaluates the patient’s oral health and creates custom-fitted trays for the whitening gel application.
Application:
The patient fills the trays with the prescribed bleaching gel and places them over the teeth for a designated period, often a few hours each day or overnight.
Duration:
At-home teeth whitening may take several days or weeks to achieve the desired results, depending on the concentration of the bleaching agent.
How Teeth Whitening Works: The Oxidation Process
The effectiveness of teeth whitening treatments lies in the process of oxidation. The bleaching agents used in teeth whitening treatments, hydrogen peroxide, and carbamide peroxide, contain oxygen molecules that penetrate the enamel and dentin layers of the teeth. During the oxidation process, the oxygen molecules break down the chemical bonds of the chromogens, which are the pigmented molecules responsible for tooth discoloration.
As the chemical bonds of the chromogens break down, the molecules become smaller and less pigmented. This results in the lightening of tooth color, as the smaller, less pigmented molecules are more translucent, allowing more of the natural tooth color to shine through.
The Role of Peroxide in Teeth Whitening
Hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, the active ingredients in teeth whitening bleaching agents, work through the release of oxygen molecules during the oxidation process. The peroxide molecules penetrate the tooth enamel and dentin, effectively breaking down the stains within and on the tooth surface.
a. Hydrogen Peroxide:
Hydrogen peroxide is a potent bleaching agent that directly breaks down the chemical bonds of the chromogens, resulting in significant teeth whitening effects. However, it needs to be used with caution as higher concentrations may cause tooth sensitivity or irritation to the soft tissues.
b. Carbamide Peroxide:
Carbamide peroxide is a stable compound that breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea. Its slower release of hydrogen peroxide allows for longer contact time with the teeth, making it suitable for at-home teeth whitening kits.
Effectiveness of Teeth Whitening Treatments
Teeth whitening treatments have shown to be highly effective in removing stains and discoloration from the teeth. The level of effectiveness can vary based on factors such as the type and severity of tooth discoloration, the concentration of the bleaching agent, the method of application, and the individual’s oral health.
Professional teeth whitening treatments performed in a dental office typically yield more immediate and dramatic results due to the higher concentration of the bleaching agent and the use of special activation techniques. On the other hand, at-home teeth whitening kits, although less potent, can still produce significant improvements in tooth color over a longer period.
The Importance of Professional Supervision
While teeth whitening can be an effective and safe cosmetic procedure, professional supervision is crucial to ensure proper treatment and prevent potential complications. Dental professionals can accurately assess the patient’s oral health, determine the most suitable treatment approach, and monitor the whitening process to avoid overexposure to the bleaching agent.
Additionally, professional supervision helps address any potential side effects or tooth sensitivity that may occur during or after the teeth whitening procedure. The dentist can provide recommendations for managing sensitivity and ensure the patient achieves the desired results safely and effectively.
Considerations and Limitations
It’s essential to recognize that teeth whitening may not be suitable for everyone or may not yield the desired results in all cases. Considerations and limitations of teeth whitening include:
a. Existing Dental Restorations:
Teeth whitening treatments may not change the color of dental restorations such as dental crowns, bridges, or fillings. In such cases, the restorations may need replacement to match the newly whitened natural teeth.
b. Tooth Sensitivity:
Some individuals may experience temporary tooth sensitivity during or after teeth whitening. Dental professionals can provide desensitizing agents or recommend specific products to manage sensitivity.
c. Tetracycline Stains:
Certain types of tooth discoloration, such as tetracycline stains, may be more challenging to whiten and may require alternative cosmetic dental procedures like dental bonding or veneers.
d. Overuse:
Excessive use or overuse of teeth whitening products, especially those with high concentrations of bleaching agents, can lead to tooth sensitivity, enamel erosion, or gum irritation. Professional supervision is critical to prevent these issues.
Conclusion
Teeth whitening is a popular and effective cosmetic dental procedure that can significantly enhance a person’s smile and confidence. The science behind teeth whitening relies on the oxidation process facilitated by the bleaching agents, hydrogen peroxide, and carbamide peroxide. These agents break down the pigmented molecules responsible for tooth discoloration, resulting in a lighter and brighter smile.
It’s essential to seek professional supervision when considering teeth whitening to ensure the treatment is appropriate for the individual’s oral health and to monitor the process safely. Teeth whitening can be a game-changer for achieving a more vibrant and youthful smile, but it’s equally crucial to practice good oral hygiene and adopt habits that help maintain the results over time.


